Vol. 13, No. 5 • May 2020
Dear Colleagues:
 Welcome to the May 2020 issue of The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. We begin the issue with a retrospective analysis from Patel et al, in which the authors investigated the efficacy of fixed-combination calcipotriene 0.005% plus betamethasone dipropionate 0.064% (Cal/BD) foam for the treatment of scalp psoriasis. In this post-hoc analysis of data from a Phase II, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study of Cal/BD foam, the authors found that patients achieved greater improvements in their scalp psoriasis with Cal/BD foam versus BD or Cal foam alone at Week 4 when considering modified Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (mPASI), proportion of patients with reduction of 50 percent or greater in total sign score, and proportion of patients with at least a 75-percent reduction in mPASI score.
Welcome to the May 2020 issue of The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology. We begin the issue with a retrospective analysis from Patel et al, in which the authors investigated the efficacy of fixed-combination calcipotriene 0.005% plus betamethasone dipropionate 0.064% (Cal/BD) foam for the treatment of scalp psoriasis. In this post-hoc analysis of data from a Phase II, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study of Cal/BD foam, the authors found that patients achieved greater improvements in their scalp psoriasis with Cal/BD foam versus BD or Cal foam alone at Week 4 when considering modified Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (mPASI), proportion of patients with reduction of 50 percent or greater in total sign score, and proportion of patients with at least a 75-percent reduction in mPASI score.
Next, in a case series by Rullan et al, the authors propose a novel treatment of acne scarring using a multimodal approach comprising chemical reconstruction of skin scars, subcision, and microneedling. The authors conducted a retrospective chart review that included 139 patients who were treated with a combination of the three procedures. On average, the patients received a total of two treatments each, and this combination approach to treating acne scars resulted in consistently high satisfaction among patients and photographic evidence of improvements.
After, in a brief report from Xiao et al, the authors discuss treating the perioral region with hyaluronic acid fillers. First, the authors review the perioral anatomy and current percutaneous filler injection techniques for perioral cosmesis. They then present a novel intraoral filler injection approach; the authors report that this technique improves perioral aesthetics with minimal downtime and high patient satisfaction.
Following this, in a brief report from Marson and Baldwin, the authors present a modified technique for the excision of dumbbell-shaped keloids on the earlobe using a #15 blade and punch biopsy. According to the authors, this technique, when combined with continual compression earrings and intralesional corticosteroids, results in excellent cosmetic outcomes and minimal recurrence.
Afterward, we present two case reports. In the first case report, from Tuknayat et al, the authors report a case of a 50-year-old woman with nasopharyngeal mantle cell lymphoma metastasizing to the skin. The second case report, from Schuler et al, describes a 33-year-old man with folliculitis induced by laser hair removal; the authors provide strategies for managing laser hair removal-induced folliculitis, including prophylactic doxycycline and topical steroids as well as gentle post-procedure washing techniques to assist in depilation.
Following this, we present a review from Solway et al, in which the authors review the literature for evidence supporting the role of a whole-food, plant-based diet in the prevention and reversal of skin aging, with a focus on dietary factors that contribute to telomere length.
Finally, in the latest installment of “What’s New in the Medicine Chest?” by Del Rosso, the author provides an update on the latest developments in nonsteroidal topical therapy for atopic dermatitis. Modes of action, including phosphodiesterase-4 inhibition, aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation, and Janus kinase inhibition are discussed. Emphasis is placed on therapeutic approaches related to modes of action, with clinical data included.
We hope you enjoy this issue of JCAD. As always, we welcome your feedback and submissions.
With regards,
James Q. Del Rosso, DO, FAOCD—Editor-in-Chief, Clinical Dermatology
Wm. Philip Werschler, MD, FAAD, FAACS—Editor-in-Chief, Aesthetic Dermatology
Seemal R. Desai, MD, FAAD— Associate Editor
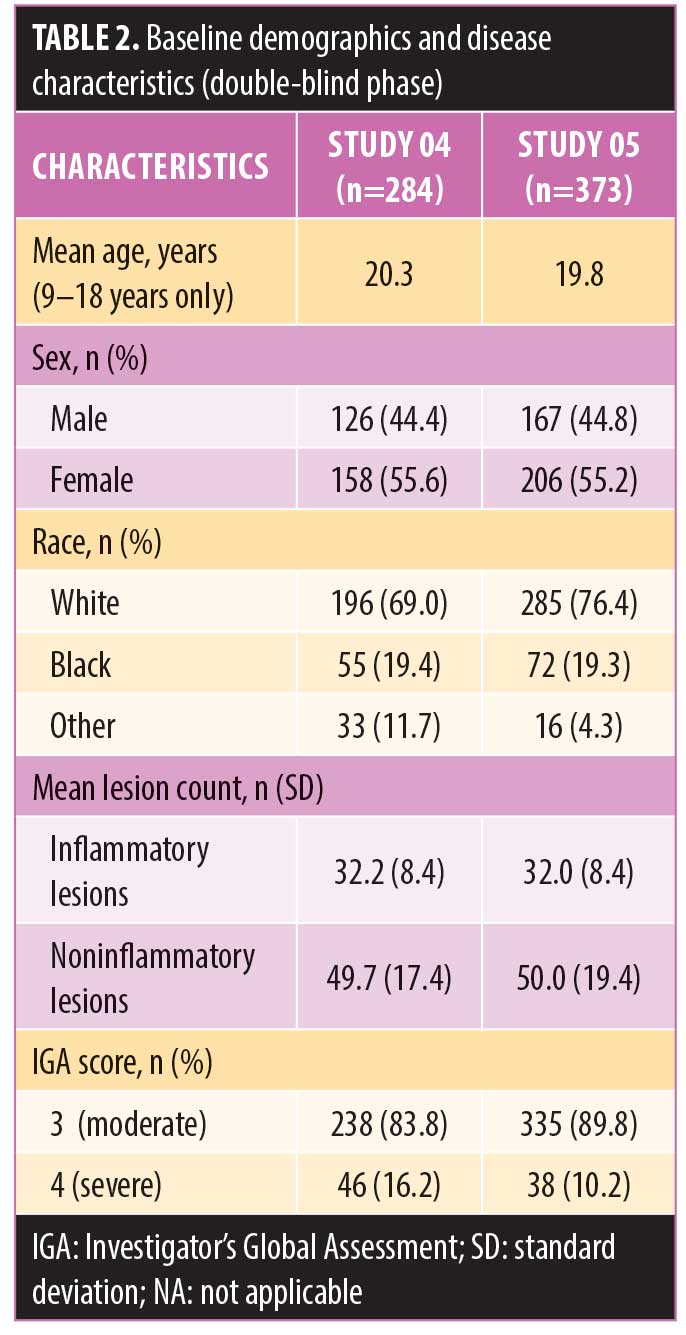
Correction
J clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020;13(6):7.
Stein Gold L, Dhawan S, Weiss J, et al. Open-label Extension Study Evaluating Long-term Safety and Efficacy of FMX101 4% Minocycline Foam for Moderate-to-Severe Acne Vulgaris [original article published in J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2019;12(10):16–23].
1. Data in the “Mean lesion count, n (SD)” row was incorrectly formatted. The corrected table is included below.